Finance Research Group
 Dr. Simon Alfano Dr. Simon Alfano |
 Daniel Drummer Daniel Drummer |
 Dr. Stefan Feuerriegel Dr. Stefan FeuerriegelResearch Group Leader |
 Dr. Joscha Märkle-Huß Dr. Joscha Märkle-Huß |
 Prof. Dr. Dirk Neumann Prof. Dr. Dirk NeumannChair Holder |
Research
Machine learning and text mining have been used for some time to forecast stock market reactions. However, knowledge on information processing by human agents facing qualitative information is rare and mostly unknown. The Finance Research Group aims to close this gap and improve the understanding of the role of textual financial news in forming investor decisions.
Spin-off: TonalityTech GmbH
Our spin-off TonalityTech GmbH provides an easy-to-use add-in for Microsoft Word for corporate communications, in particular investor relations and media relations. Our research revealed that an improved tonality of corporate communications can increase company valuation by up to 2.7%.
Our add-in makes this knowledge available to corporate communications practitioners. Thus, corporate communications practitioners can benefit from an evidence-based tool that facilitates steering the tonality and readability of corporate communication. At the same time, the add-in seamlessly integrates into existing communication creation processes.
Interested? Contact us via tonalitydumdummymy@is.dumdummymyuni-freiburg.de or visit our website.
Podcast and article by IR Magazine featuring our research
Recently, IR Magazine featured our research in a podcast in the series IR magazine asks. An article on our research is also available from IR Magazine.
Organization of FinanceCom 2016 workshop
The Chair for Information Systems Research will host the 2016 FinanceCom workshop in Frankfurt. After very successful FinanceCom workshops in Sydney, Regensburg, Montreal, Paris, Frankfurt and Barcelona, FinanceCom 2016 will be returning to Frankfurt on 8th December 2016. Advancements in Information and Communication Technologies have paved the way to new business models, markets, networks, services, and players in the financial services industry.
FinanceCom 2016 invites papers that help to understand, drive and exploit the associated systems, technologies and opportunities.
http://www.financecom2016.is.uni-freiburg.de
Project: Dictionary Generation for Financial News
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
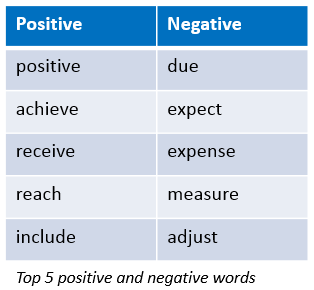
Pröllochs N, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Generating Domain-Specific Dictionaries Using Bayesian Learning, 23rd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2015), Münster, Germany, May 26-29, 2015.
Pröllochs N, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Say it Right – How Managers Prettify Corporate Disclosures 2015 (Winter Conference on Business Intelligence (WCBI 2015), Snowbird, Utah, 12-14 March 2015.
Pröllochs N, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Is Human Information Processing Affected by Emotional and Cognitive Biases? Evidence from the Stock Market, Working Paper, University of Freiburg, 2015.
Project: Information Processing of Initial Public Offering Filings
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
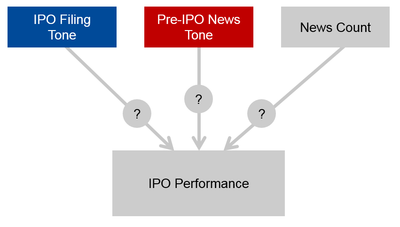
Feuerriegel S, Schmitz J T, Pröllochs N, Neumann D: What Matters Most? How Tone in Initial Public Offering Filings and Pre-IPO News Influences Stock Market Returns What Matters Most? How Tone in Initial Public Offering Filings and Pre-IPO News Influences Stock Market Returns 2015 (2015 FMA European Conference, Venice, Italy, June 11-12, 2015.
Feuerriegel S, Schmitz J T, Neumann D: What Matters Most? How Tone in Initial Public Offering Filings and Pre-IPO News Influences Stock Market Returns, Working Paper, University of Freiburg, 2014.
Project: News Reception Compared Across Extracted Topics
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
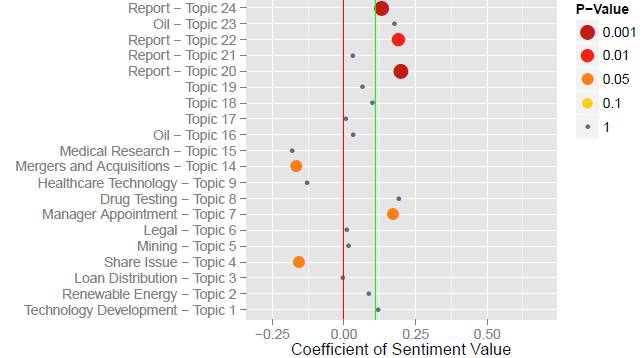
Feuerriegel S, Ratku A, Neumann D: Which News Disclosures Matter? News Reception Compared Across Topics Extracted from the Latent Dirichlet Allocation, Working Paper, University of Freiburg, 2015.
Feuerriegel S, Ratku A, Neumann D: Analysis of How Underlying Topics in Financial News Affect Stock Prices Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation, Working Paper, University of Freiburg, 2014.
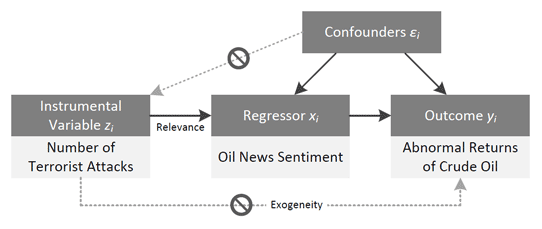
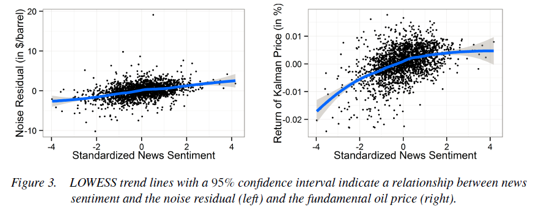
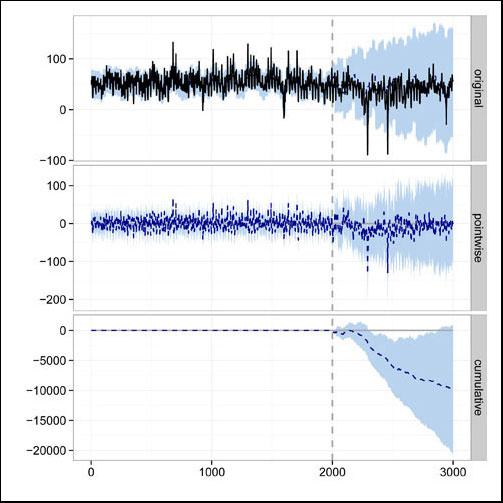
Project: Speculation & Irrational Exuberance in Oil Markets
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
Jandl J, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Long- and Short-Term Impact of News Messages on House Prices: A Comparative Study of Spain and the United States, 2014 (35th International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2014), Auckland, New Zealand, 14-17 December 2014, Completed Research Paper).
Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: News or Noise? How News Drives Commodity Prices, 2013 (34th International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2013), Milan, Italy, 15-18 December 2013, Completed Research Paper).
Feuerriegel S, Lampe M W, Neumann D: News Processing during Speculative Bubbles: Evidence from the Oil Market, 2014 (47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Waikoloa, Big Island, January 6-9, 2014, IEEE Computer Society).
Feuerriegel S, Ratku A, Neumann D: Finding Evidence of Irrational Exuberance in the Oil Market, Working Paper, University of Freiburg, 2014.
Project: News Reception in Accordance with the Noise Trader Theory
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
Alfano S, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Is News Sentiment More than Just Noise?, 23rd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2015), Münster, Germany, May 26-29, 2015.
Alfano S, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Do Pessimists Move Asset Prices? Evidence from Applying Prospect Theory to News Sentiment, Working Paper, University of Freiburg 2015.
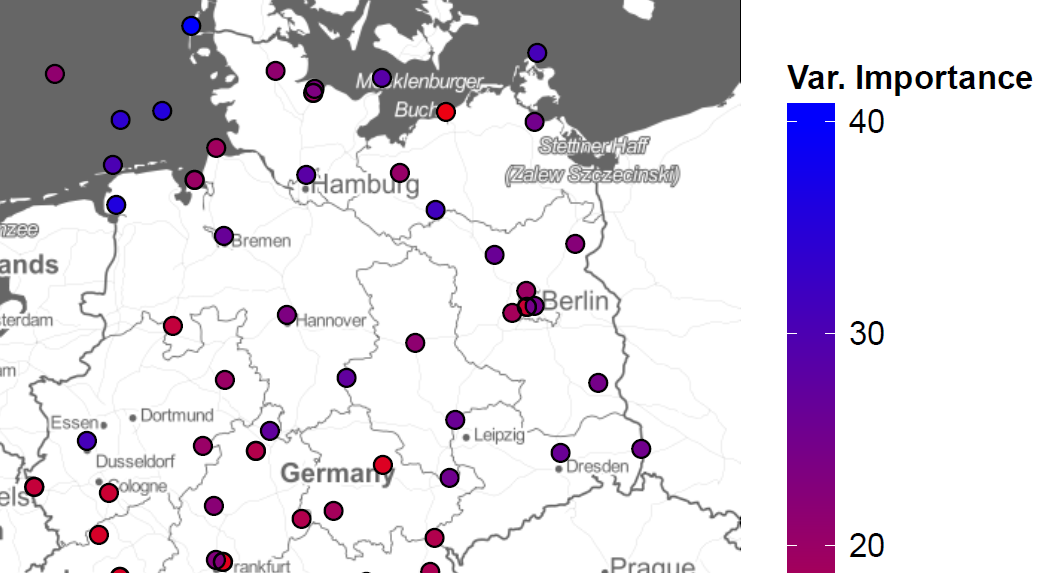
Project: Electricity Price Forecasting
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
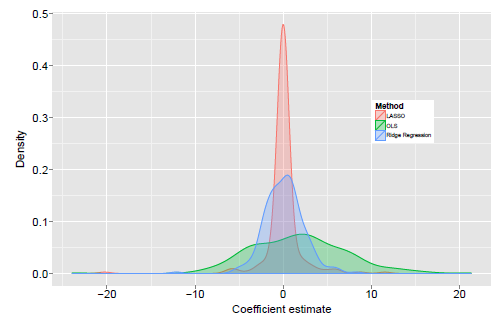
Ludwig N, Feuerriegel S, Neumann D: Putting Big Data Analytics to Work: Feature Selection for Forecasting Electricity Prices using the LASSO and Random Forests, Journal of Decision Systems, 2015: 24(1).
Feuerriegel S, Riedlinger S, Neumann D: Predictive Analytics for Electricity Prices using Feed-Ins from Renewables, 2014 (22nd European Conference on Information Systems (ECIS 2014), Tel Aviv, Israel, June 9-11, 2014, Complete Research Paper).
Project: Electricity Auction Design in Germany
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|
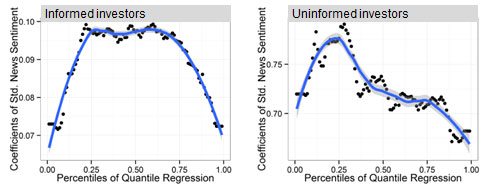
Project: Asymmetric Information Processing of Financial News Sentiment
| Aims |
|
| Method |
|
| Results |
|